Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces insufficient thyroid hormones. This can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, and constipation. It is often caused by autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto's thyroiditis or iodine deficiency. Diagnosis involves blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels. Treatment typically includes daily oral medication, such as levothyroxine, to normalize hormone levels and manage symptoms. Regular monitoring ensures effective management and adjustment of medication as needed.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland overproduces thyroid hormones, accelerating the body's metabolism. Symptoms include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, sweating, nervousness, and frequent bowel movements. Common causes are Graves' disease, thyroid nodules, or inflammation. Diagnosis is confirmed through blood tests measuring hormone levels and imaging studies. Treatment options include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy to destroy overactive thyroid cells, or surgery to remove part of the thyroid. Proper management helps control symptoms and prevent complications.
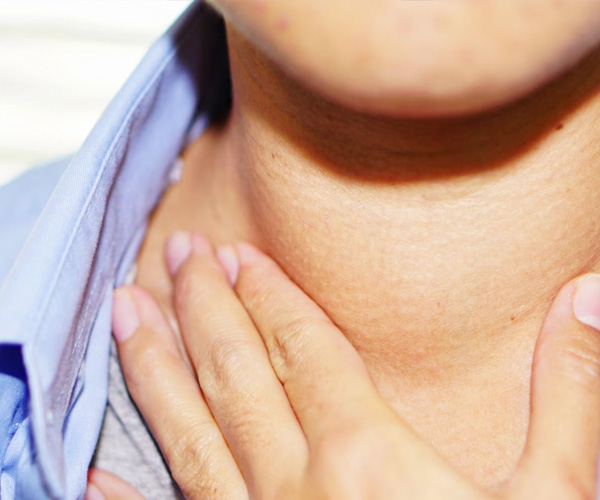
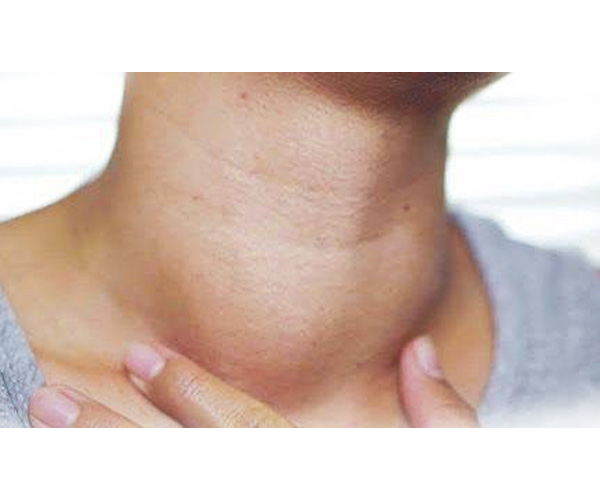
Thyroid Nodules and Cysts
Thyroid nodules are abnormal lumps in the thyroid gland, often benign but sometimes requiring evaluation for cancer. Cysts are fluid-filled nodules that can cause swelling or discomfort. Diagnosis involves physical examination, ultrasound, and sometimes biopsy. Most nodules and cysts are harmless and monitored over time. Treatment depends on size, symptoms, and any cancer risk, ranging from observation to surgical removal.
Multinodular Goiter
Multinodular goiter is an enlarged thyroid gland with multiple nodules, which may be benign or, rarely, cancerous. Symptoms include neck swelling, difficulty swallowing, or breathing issues. Diagnosis involves ultrasound and sometimes thyroid function tests or biopsy. Treatment may include medication, radioactive iodine, or surgery, depending on nodule size, symptoms, and risk of cancer.
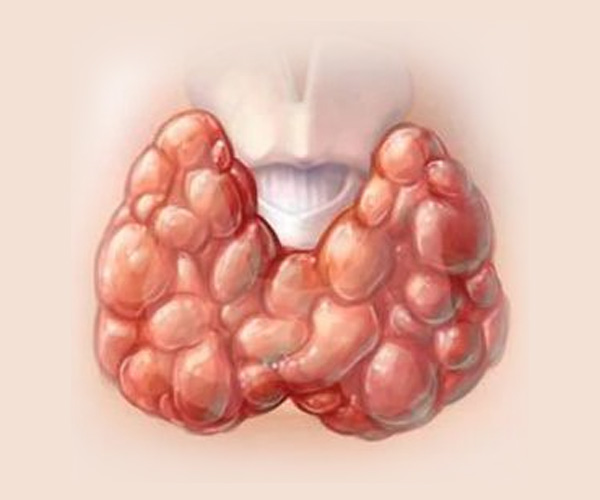

Graves Disease
Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder that leads to hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid gland overproduces thyroid hormones. This condition is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism and predominantly affects women, typically between the ages of 30 and 50. The exact cause of Graves' disease is not fully understood, but it involves a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors. The immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, causing it to become overactive. Symptoms of Graves' disease include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, increased appetite, nervousness, irritability, sweating, and heat sensitivity.
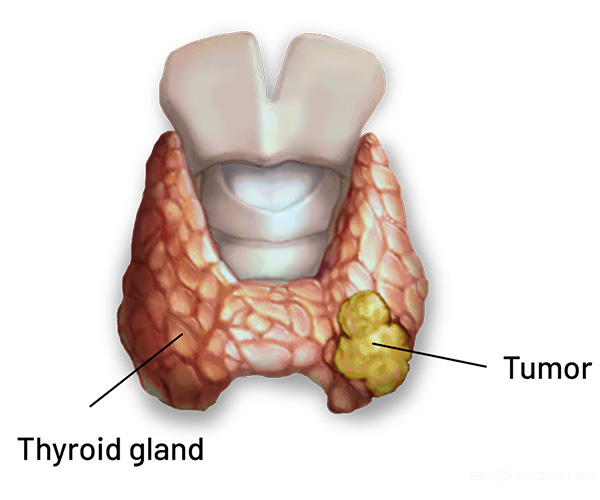
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer originates in the thyroid gland and includes types like papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic. Common symptoms are a neck lump, voice changes, swallowing difficulties, and neck pain. Diagnosis involves physical exams, ultrasound, fine-needle aspiration biopsy, and blood tests. Treatment options include surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, hormone therapy, radiation, or chemotherapy, based on the cancer type and stage. Early detection and treatment typically lead to good outcomes, as many thyroid cancers are highly treatable.
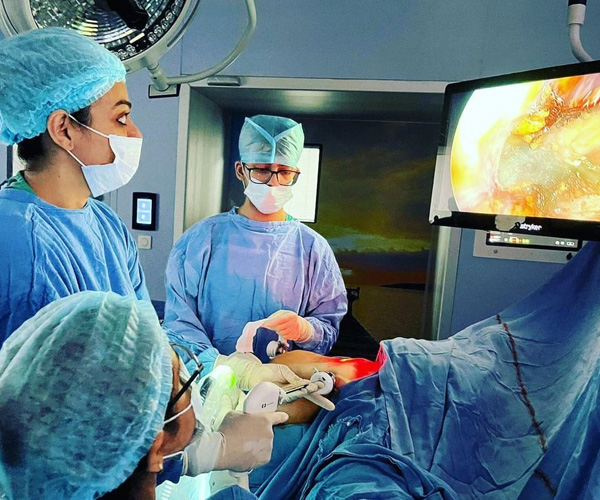
Endoscopic Thyroidectomy
Removing a thyroid gland surgically may cause a scar on the neck. Endoscopic thyroidectomy is a novel technique of thyroidectomy that leaves no visible scar. The surgery can be performed by an expert surgeon in this field with the help of an endoscope. The access is from the axilla on one or both sides where a very small incision is made. The camera gives a magnified view. The risks associated with this surgery are same as in open surgery.
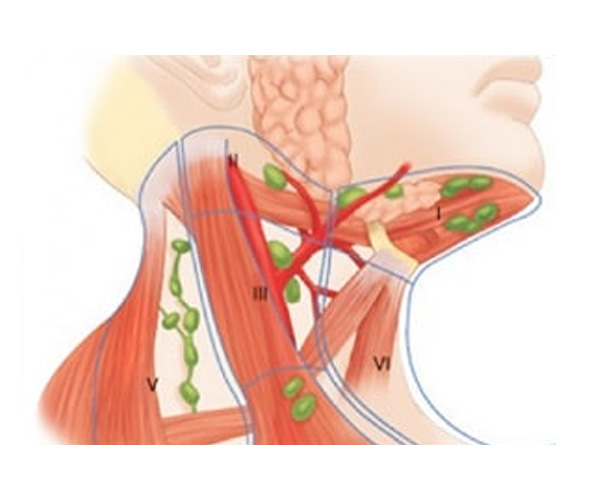
Neck Dissection
Neck dissection is a surgical procedure to remove lymph nodes and surrounding tissue in the neck to treat or prevent the spread of cancer, particularly head and neck cancers. Types include radical, modified radical, and selective, depending on the extent of tissue removal. The surgery aims to ensure complete cancer removal while preserving as much function as possible. Postoperative care includes monitoring for complications and physical therapy to regain neck movement and strength.