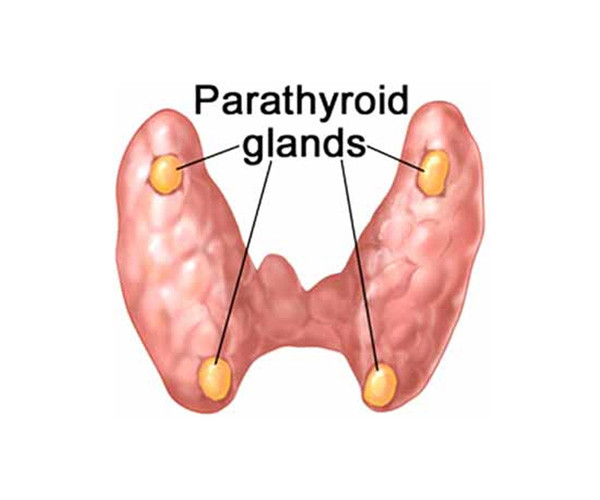
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition where overactive parathyroid glands secrete excessive parathyroid hormone, leading to high calcium levels in the blood. Symptoms include bone pain, kidney stones, fatigue, depression, and digestive issues. Causes include parathyroid adenoma, hyperplasia, or carcinoma. Diagnosis involves blood tests for calcium and PTH levels, and imaging studies. Treatment options include surgical removal of the overactive glands or medication to manage symptoms and control calcium levels.
Parathyroid Adenoma
Parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the parathyroid gland causing overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH). This leads to hypercalcemia, with symptoms like bone pain, kidney stones, fatigue, and abdominal pain. Diagnosis involves blood tests for elevated calcium and PTH levels, along with imaging studies. Treatment typically involves surgical removal of the adenoma, which usually resolves symptoms and normalizes calcium levels. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and maintain health.
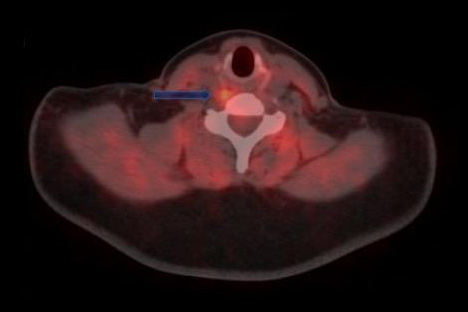
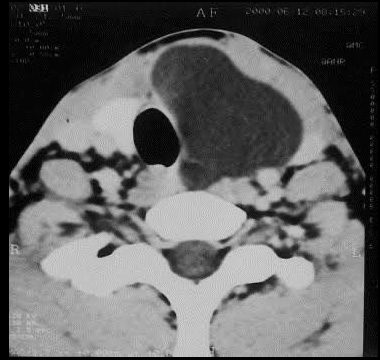
Parathyroid Cysts
Parathyroid cysts are rare, fluid-filled sacs in the parathyroid glands. They can cause neck swelling and may affect hormone levels, leading to hyperparathyroidism. Diagnosis involves blood tests, ultrasound, and fine-needle aspiration. Most cysts are benign and asymptomatic, requiring monitoring. Symptomatic or large cysts may need surgical removal to prevent complications and normalize hormone levels.
Parathyroid Hyperplasia
Parathyroid hyperplasia is the enlargement of all four parathyroid glands, leading to excess parathyroid hormone production and hypercalcemia. This can result in symptoms such as bone pain, kidney stones, fatigue, and digestive issues. It is often associated with genetic conditions like multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes. Diagnosis involves blood tests for elevated calcium and PTH levels, and imaging studies. Treatment typically includes surgical removal of most or all of the hyperplastic glands to normalize hormone levels and prevent complications.