Mastectomy
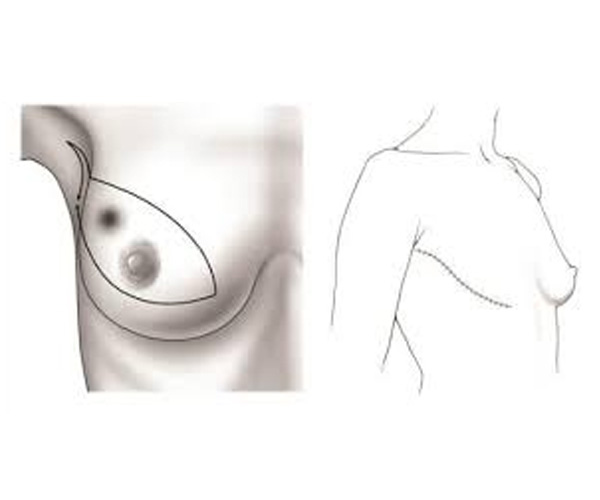
A mastectomy is a surgical procedure to remove one or both breasts, either partially or completely, primarily for treating or preventing breast cancer. Types include total, modified radical, and radical mastectomy, varying in extent of tissue removal. Factors influencing the decision include cancer type, stage, genetic risk, and patient preference. Reconstructive surgery often follows, using implants or autologous tissue. The decision for mastectomy involves careful consideration and discussion with healthcare providers to ensure it meets the patient's medical and personal needs.
Breast Conserving Surgery
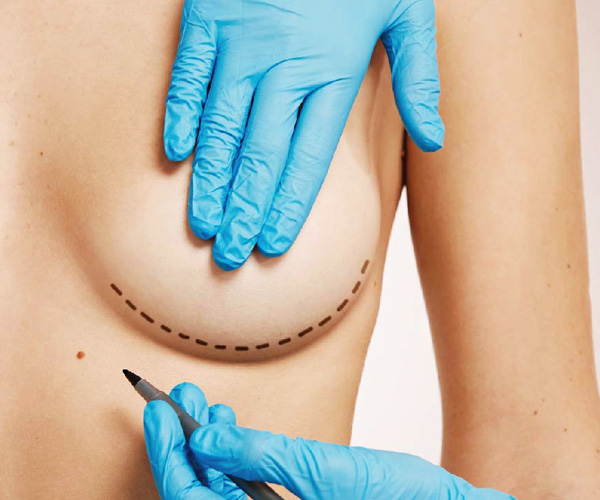
Breast-conserving surgery, also known as a lumpectomy or partial mastectomy, involves removing the cancerous part of the breast tissue while preserving most of the breast. BCS is suitable for early-stage breast cancer and aims to maintain breast appearance and sensation. The decision for BCS depends on the tumor size, location, breast size, and patient preference, with careful discussion with healthcare providers to ensure optimal outcomes.
Oncoplasty
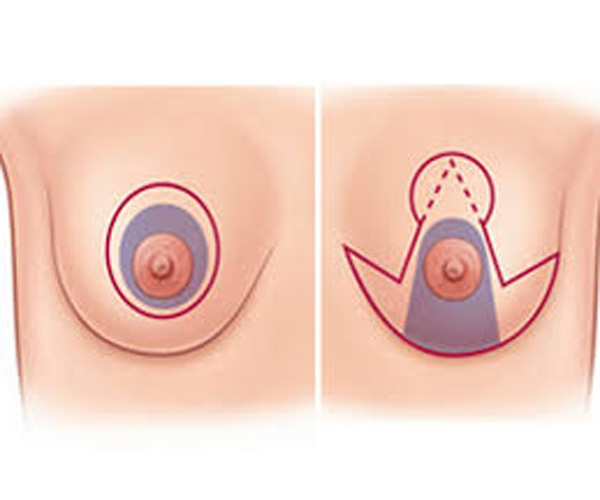
Oncoplasty combines oncologic breast cancer surgery with plastic surgery techniques to remove tumors while preserving or enhancing breast appearance. This approach involves reshaping the remaining breast tissue and often includes techniques like tissue rearrangement, reduction, or lift. Oncoplasty aims to achieve optimal cancer control and aesthetic outcomes, improving the patient's quality of life. It is suitable for various breast cancer stages and is tailored to individual needs, requiring an expert breast oncoplastic surgeon.
Sentinel Lymph Node Dissection
Sentinel lymph node dissection is a surgical procedure used to stage and treat certain cancers, particularly breast cancer and melanoma. It involves removing the sentinel lymph node, the first node to which cancer cells are likely to spread from the primary tumor. This node is identified using a tracer substance. Analyzing the sentinel node helps determine if cancer has spread, guiding further treatment decisions. It is less invasive than traditional lymph node removal, reducing complications and recovery time.
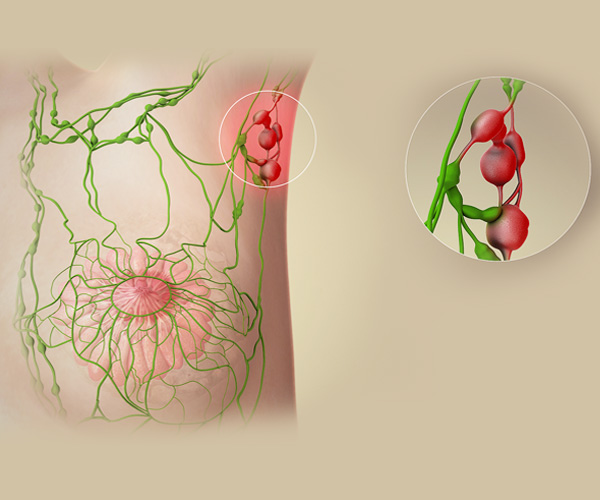
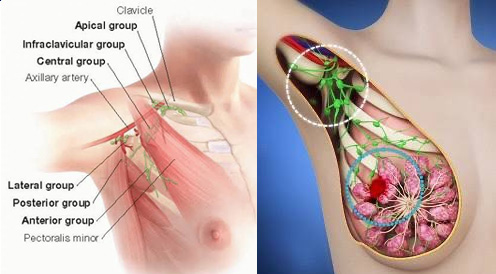
Axillary Sampling
Axillary sampling is a surgical procedure where a small number of lymph nodes are removed from the axilla (underarm area) to check for the spread of breast cancer. Unlike full axillary lymph node dissection, this procedure removes only a few nodes to reduce the risk of complications like lymphedema. The sampled nodes are examined for cancer cells, which helps in staging the cancer and planning further treatment. This method aims to balance accurate cancer staging with minimizing patient side effects.
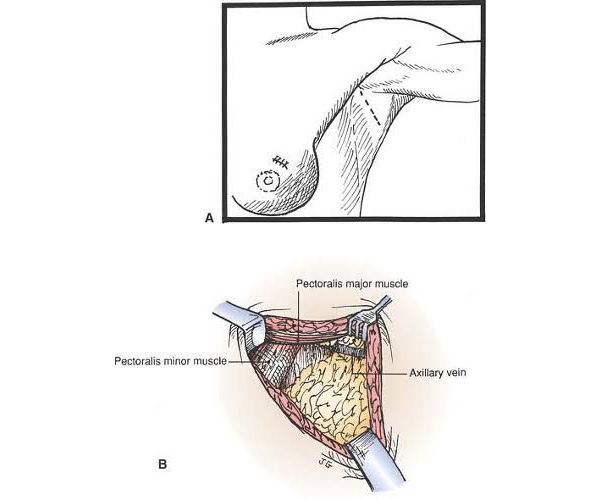
Axillary Clearance
Axillary clearance, also known as axillary lymph node dissection, is a surgical procedure to remove most or all lymph nodes from the axilla (underarm area) to treat or assess the spread of breast cancer. This procedure is typically performed when cancer is confirmed or strongly suspected to have spread to these nodes. While it provides detailed information for staging and treatment planning, axillary clearance carries risks such as lymphedema, numbness, and restricted shoulder movement, requiring careful consideration and postoperative care.
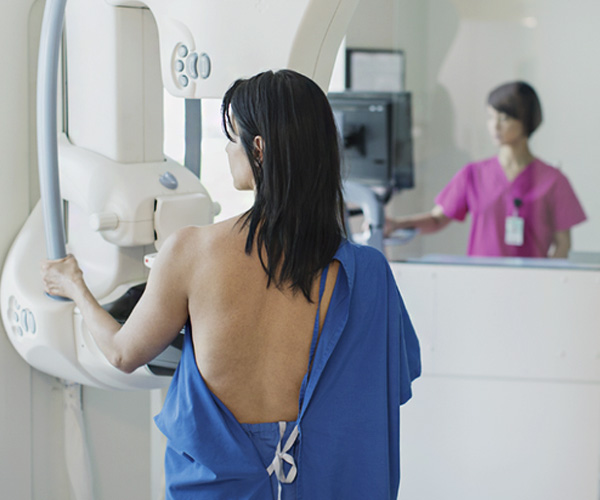
Breast Cancer Screening
Breast cancer screening involves using tests such as mammograms, ultrasound, and MRI to detect breast cancer early, before symptoms develop. Early detection increases the chances of successful treatment and survival. Screening is typically recommended for women starting at age 40, with frequency depending on individual risk factors like family history and genetic predisposition. Discussing a personalized screening plan with your healthcare provider ensures appropriate and timely monitoring, helping to catch any potential issues as early as possible.
Genetic & Hereditary Counselling
Genetic and hereditary counseling involves assessing the risk of inherited conditions through family history and genetic testing. Genetic counselors provide information, support, and guidance to individuals and families about the implications of genetic disorders. They help clients understand their risks, discuss preventive measures, and make informed decisions about their health and family planning. This counseling is crucial for conditions like cancer, heart disease, and rare genetic disorders, offering personalized risk assessments and facilitating early interventions to improve health outcomes.
Important Link
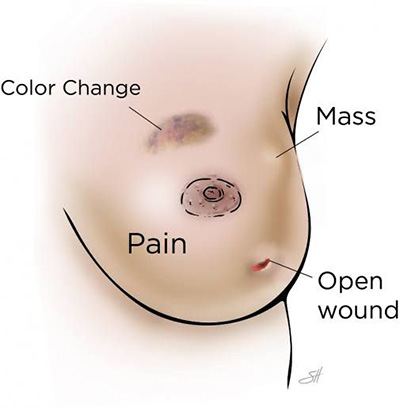
Graulomatous Mastitis
It is an atypical inflammatory condition of the breast. It may be due to complications of tuberculosis or sarcoidosis or it may be IGM Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. They present as lump or pus or discharging sinuses. Diagnosis is by clinical examination, imaging and biopsy. Thye may mimick cancer in the breast. Treatment can be complete with medications and in some cases, a surgery may be required.
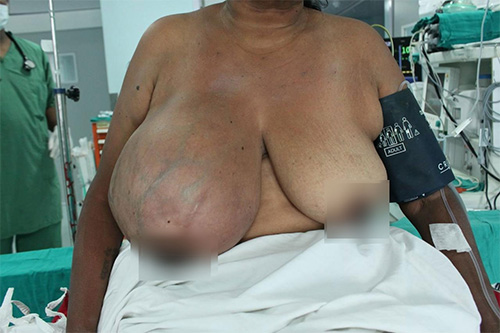
Phylloides Tumour
This is a rare tumour of the breast. It presents as a lump in the breast that is rapidly growing. It may grow to enormous size within days. One. It may look like a fibroadenoma or cancer on examination and imaging. Phylloides tumours may be benign or malignant. Urgent surgical treatment is required in these cases.